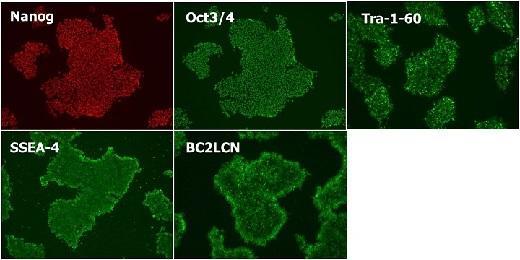
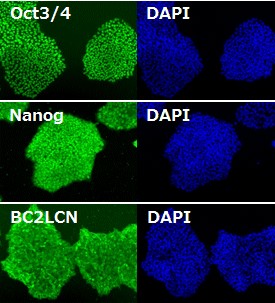
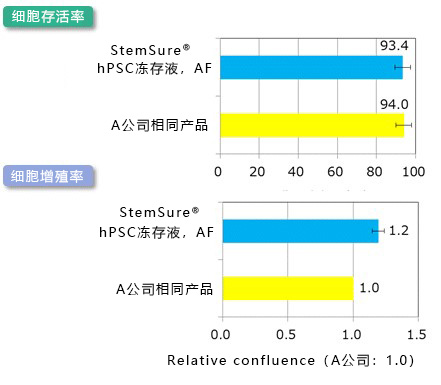
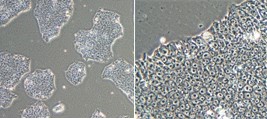
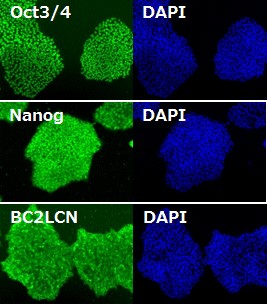
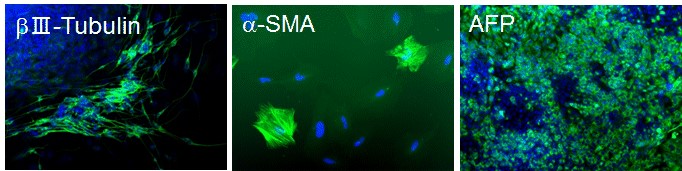
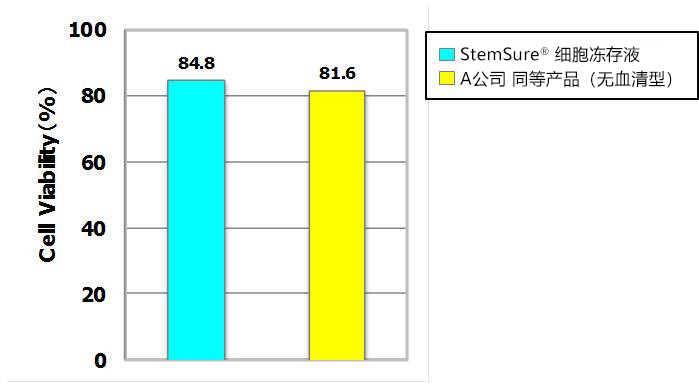
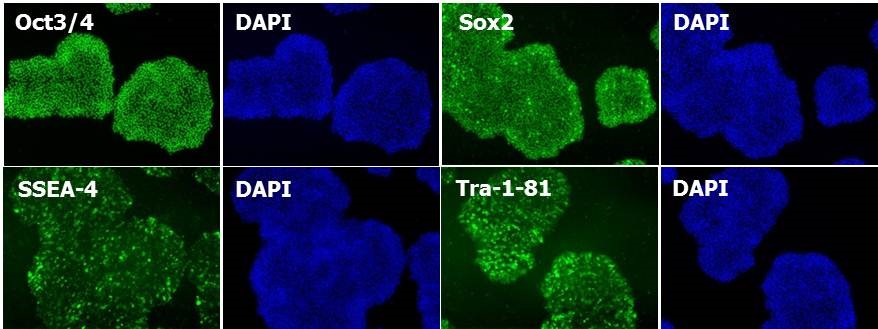
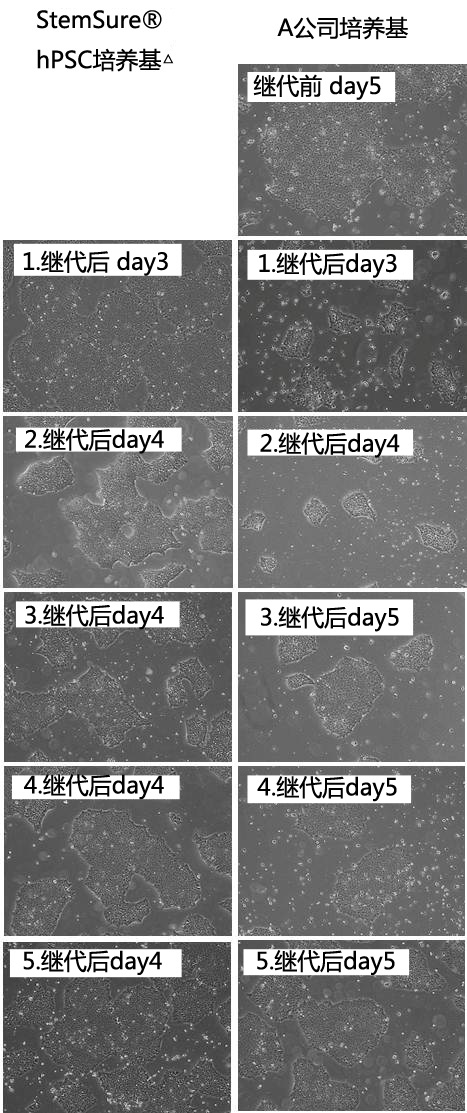
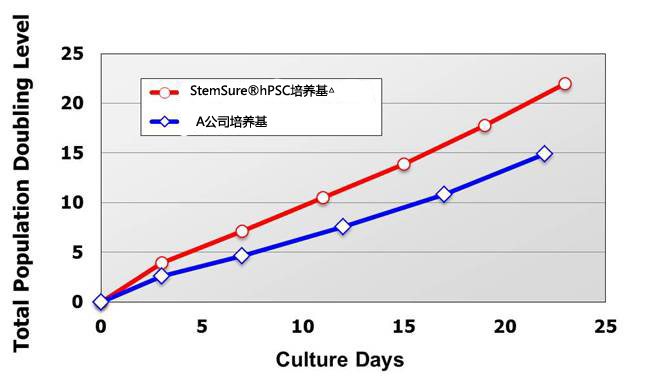
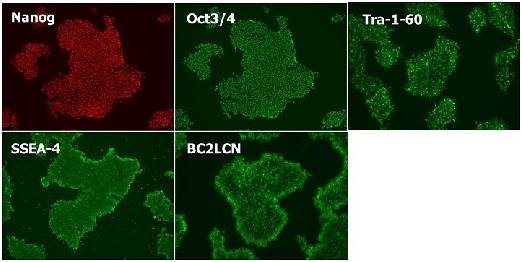
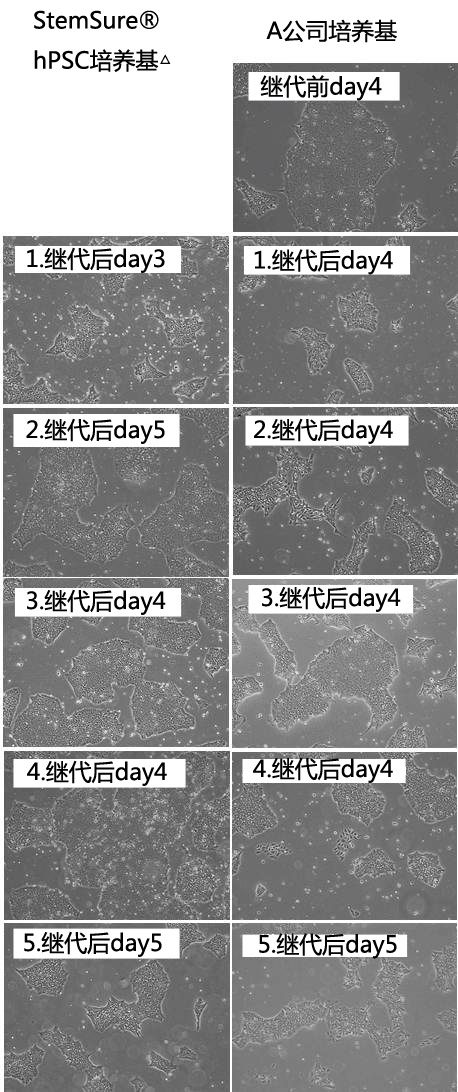
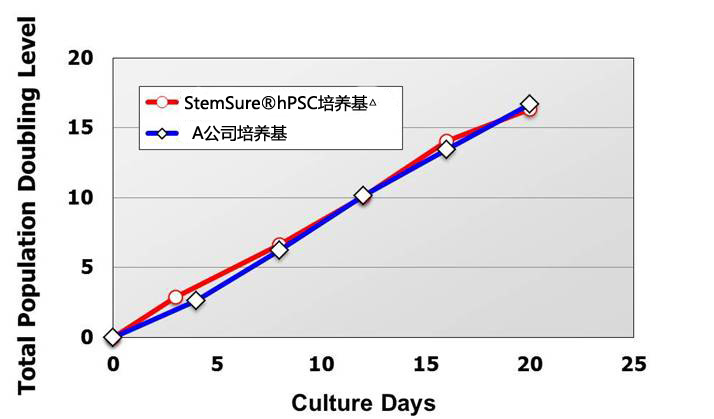
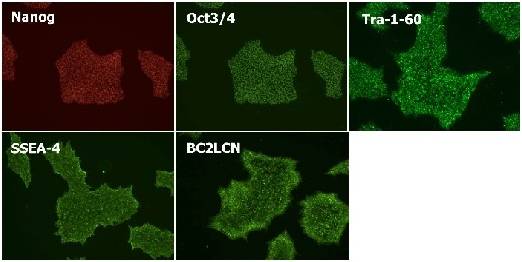
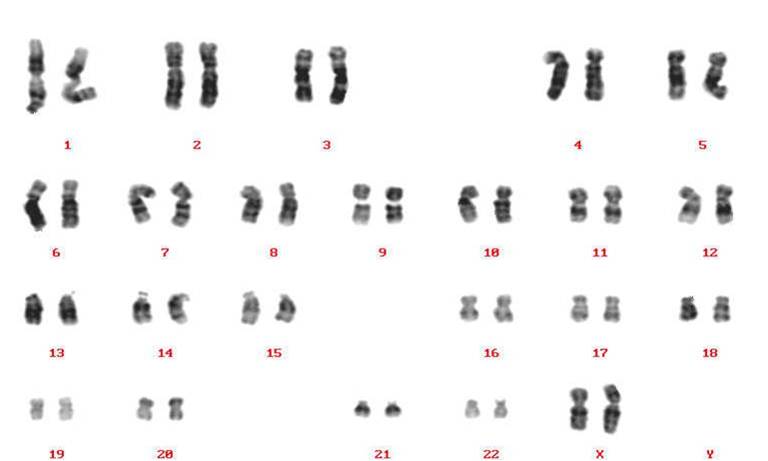
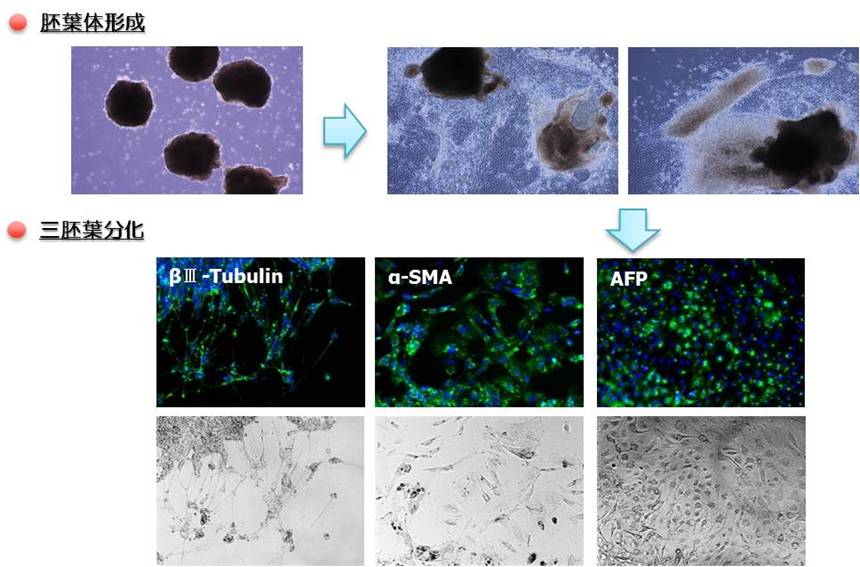
|
1.
|
Obora, K., Onodera, Y., Takehara, T., Frampton, J., Hasei, J., Ozaki, T., … & Fukuda, K. (2017). Inflammation-induced miRNA-155 inhibits self-renewal of neural stem cells via suppression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) expression. Scientific reports, 7, 43604.【mouse neural stem cell (NSC)】
|
|
2.
|
Aihara, A., Koike, T., Abe, N., Nakamura, S., Sawaguchi, A., Nakamura, T., … & Eto, K. (2017). Novel TPO receptor agonist TA-316 contributes to platelet biogenesis from human iPS cells. Blood advances, 1(7), 468-476.
|
|
3.
|
Katayama, M., Kiyono, T., Kuroda, K., Ueda, K., Onuma, M., Shirakawa, H., & Fukuda, T. (2019). Rat-derived feeder cells immortalized by expression of mutant CDK4, cyclin D, and telomerase can support stem cell growth. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 1866(5), 945-956.
|
|
4.
|
Katayama, M., Hirayama, T., Horie, K., Kiyono, T., Donai, K., Takeda, S., … & Fukuda, T. (2016). Induced pluripotent stem cells with six reprogramming factors from prairie vole, which is an animal model for social behaviors. Cell transplantation, 25(5), 783-796.【prairie vole-derived iPSCs(pv-iPSCs)】
|
|
5.
|
Kawata, M., Taniguchi, Y., Mori, D., Yano, F., Ohba, S., Chung, U. I., … & Saito, T. (2017). Different regulation of limb development by p63 transcript variants. PloS one, 12(3), e0174122.【基因编辑小鼠iPS细胞】
|
|
6.
|
Bui, P. L., Nishimura, K., Mondejar, G. S., Kumar, A., Aizawa, S., Murano, K., … & Ito, Y. (2019). Template Activating Factor-I α Regulates Retroviral Silencing during Reprogramming. Cell reports, 29(7), 1909-1922. 【Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) 】
|
|
7.
|
Sumi, S., Kawagoe, M., Abe, R., Yanai, G., Yang, K. C., & Shirouzu, Y. (2017). A multiple-funnels cell culture insert for the scale-up production of uniform cell spheroids. Regenerative therapy, 7, 52-60.
|
|
8.
|
古田明日香, & 中村肇伸. (2019). ES 細胞は代謝シフトを介して全能性細胞へと変化する. In 日本繁殖生物学会 講演要旨集 第 112 回日本繁殖生物学会大会 (pp. AW1-5). 日本繁殖生物学会.
|
|
9.
|
Onozato, D., Yamashita, M., Nakanishi, A., Akagawa, T., Kida, Y., Ogawa, I., … & Matsunaga, T. (2018). Generation of intestinal organoids suitable for pharmacokinetic studies from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 46(11), 1572-1580.
|
|
10.
|
Hayashi, Y., Matsumoto, J., Kumagai, S., Morishita, K., Xiang, L., Kobori, Y., … & Sumaru, K. (2018). Automated adherent cell elimination by a high-speed laser mediated by a light-responsive polymer. Communications biology, 1(1), 218.【hiPSC differentiation】
|
|
11.
|
Osafune, K., Toyoda, T., Takekawa, S., Nakamura, G., & Ito, R. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/490,394.
|
|
12.
|
Kato, T., Kanemura, Y., Shofuda, T., & Fukusumi, H. (2016). U.S. Patent Application No. 14/900,975.
|
|
13.
|
Eitoku, M., Kato, H., Suganuma, N., & Kiyosawa, H. (2018). Markers associated with neuron-specific Ube3a imprinting during neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cytotechnology, 70(1), 45-53.
|
|
14.
|
Onozato, D., Yamashita, M., Fukuyama, R., Akagawa, T., Kida, Y., Koeda, A., … & Matsunaga, T. (2018). Efficient generation of Cynomolgus monkey induced pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal organoids with pharmacokinetic functions. Stem cells and development, 27(15), 1033-1045.
|
|
15.
|
Katayama, M., Hirayama, T., Kiyono, T., Onuma, M., Tani, T., Takeda, S., … & Fukuda, T. (2017). Immortalized prairie vole-derived fibroblasts (VMF-K4DTs) can be transformed into pluripotent stem cells and provide a useful tool with which to determine optimal reprogramming conditions. Journal of Reproduction and Development, 2016-164.
|
|
16.
|
Matsuyama, A., & Okura, H. (2017). U.S. Patent No. 9,644,181. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
|
|
17.
|
Tomizawa, M. (2016). Culture Medium And Method For Inducing Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells To Hepatoblasts. U.S. Patent Application No. 14/749,715.
|