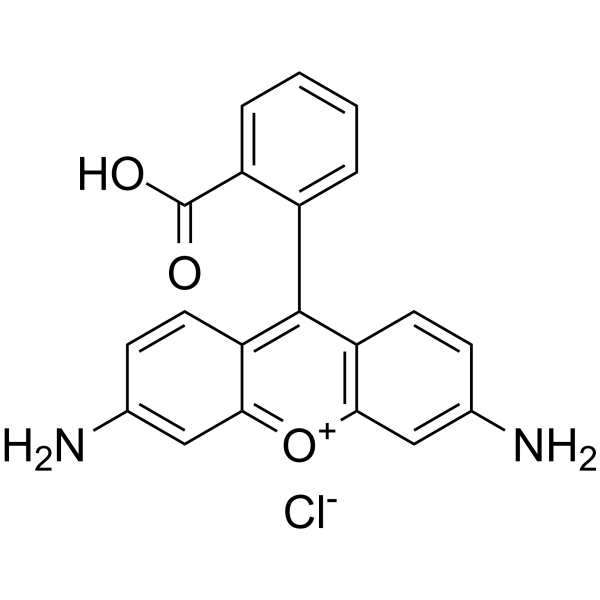
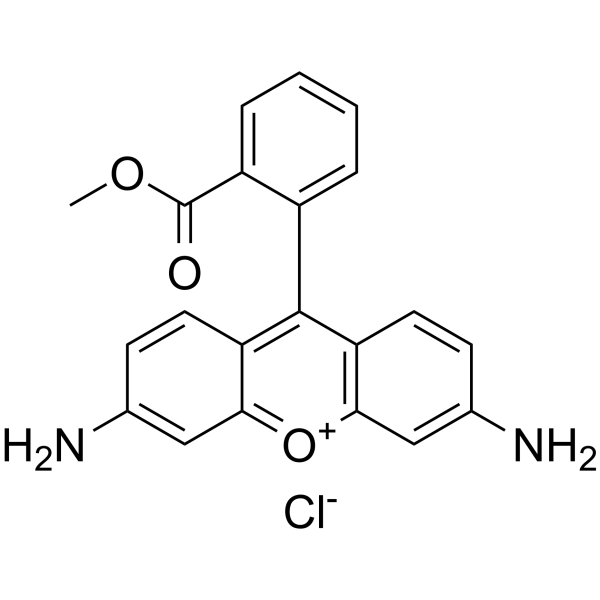
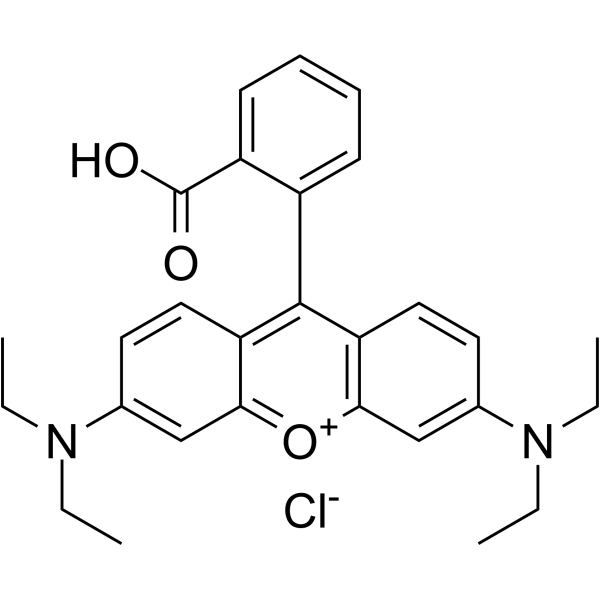
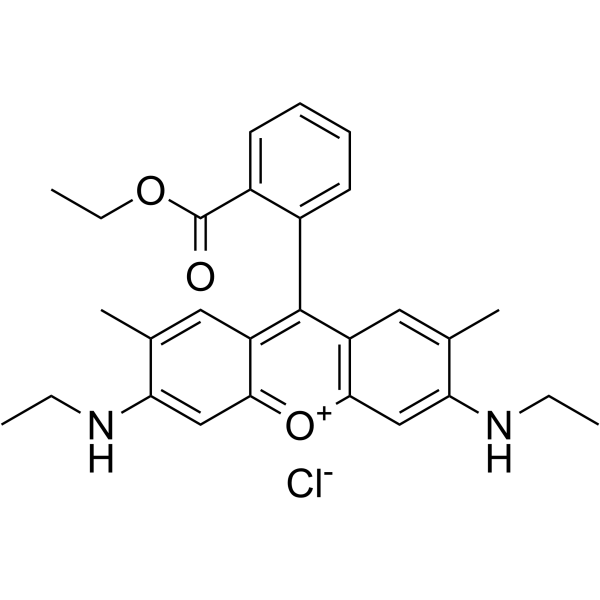
Rats[1]
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (230±20 g) are used. After the rats recovered, Rhodamine 110 in polyethylene glycol 400 (0.3 and 1 mg/mL) is administered at 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg by oral gavage. Blood samples (150 μL) are collected from the right jugular vein 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360, 480, and 720 min after drug administration. After each sampling, 100 μL of normal saline is administered via catheter to compensate for the loss of body fluid, and a 50 μL heparin solution (20 IU heparin/mL normal saline) is provided to prevent coagulation. Blood samples are centrifuged at 16,000g for 10 min at 4 °C to obtain plasma, which is stored at -20 °C until analysis. After surgery, Rhodamine 110 in polyethylene glycol 400 (1 mg/mL) is administered intravenously to rats at 3 mg/kg (n=6). A 150 μL blood sample is collected from the right jugular vein 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360, 480, and 720 min after drug administration. Then, 100 μL of normal saline is administered via the right jugular vein to compensate for body fluid loss, and 50 μL of a heparin solution (20 IU heparin/mL normal saline) is provided to prevent blood clotting.
MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only.